PACS - Picture Archiving and Communication System
Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), is a medical imaging technology used for storing, retrieving, presenting and sharing images produced by various medical hardware modalities, such as X-ray, CT scan, MRI and ultrasound machines. PACS is widely used in Radiology Departments in hospitals, Diagnostic Centers and Health Systems. In addition to sharing images within hospitals and health systems, a PACS can integrate with external health systems too.
Medical imaging has a standard format called "Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine" (DICOM). DICOM is a protocol that enables the sharing of images and other medical information. DICOM enables PACS technologies, Radiology Information Systems (RIS) to connect with and transfer health data to other healthcare system.
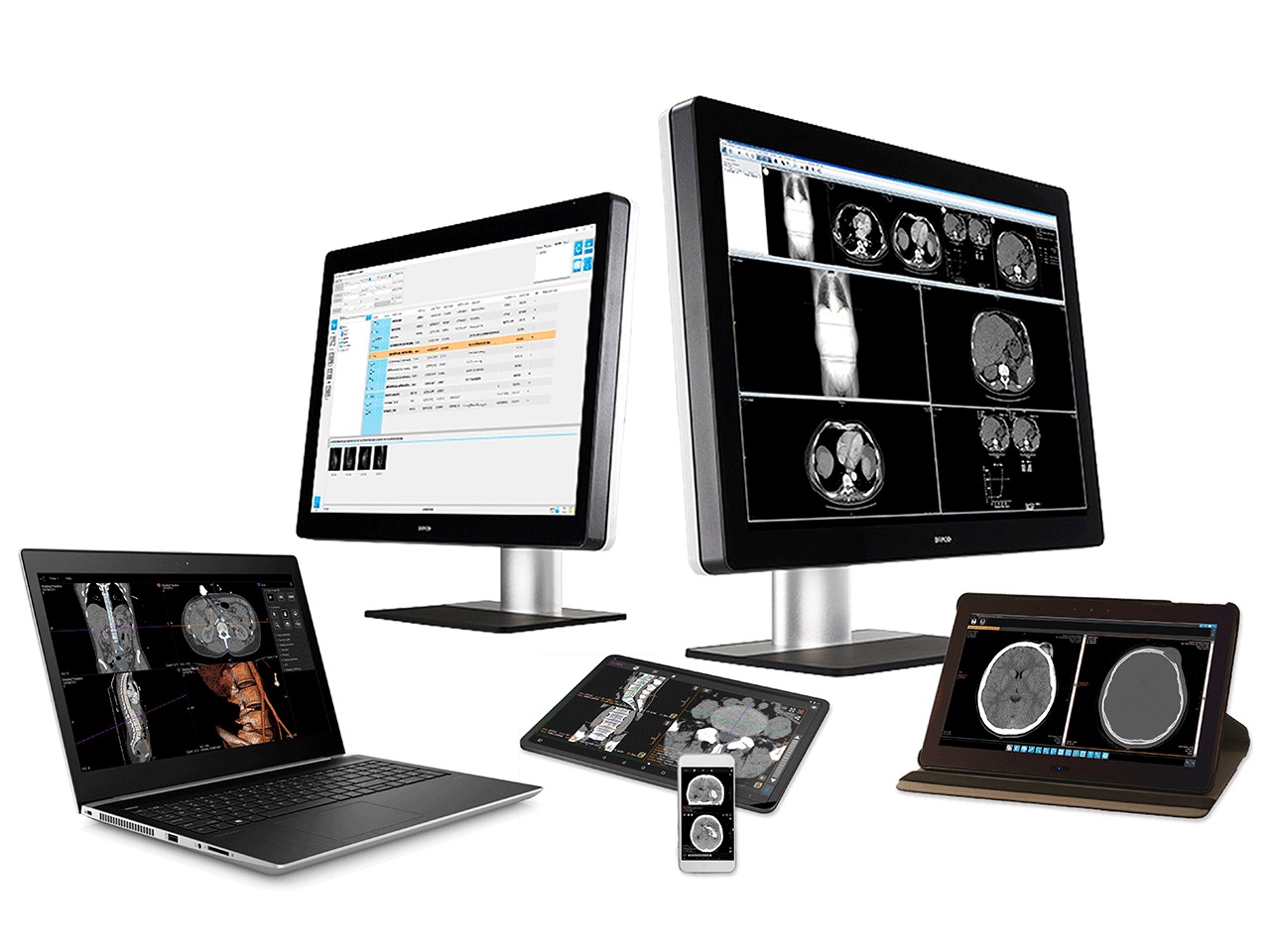
PACS Features
Salient features
- Multi-modality
- Multi-Site connectivity
- Ability to edit patient/study information
- DICOM Receive, Query/Retrieve, Storage
- Ability to merge patient records
- DICOM send, import, print, archive & burn
- CD/media
- Commit, Global Modality Work List
- DICOM Receiver
- MWL Service
- MPPS Service
- ORM / OBX listener
- PACS Broker
Advanced Features
- Cloud based PACS
- Store all images to centralised server
- Simultaneous access from multiple viewing stations
- Studies / reports viewed by physicians
- All standard DICOM viewing tools
- Derive & export old series to new
- Hanging Protocols
- HL7 and DICOM Modality Work list
- Scalable:Multi location and Multiple modality
- Fastest lossless image transfer
- Advanced processing tools
- Access through mobile
- Zero footprint web viewer
- Consistent Image quality
- Customizable User views
- Active Collaboration features


